Source: Data Dynamics. 2021. “AI in Energy: Discover How Your Data Can Be the Ultimate Game Changer! Explore 7 Reasons Why It Matters”. Available at: https://www.datadynamicsinc.com/blog-ai-in-energy-your-data-is-the-game-changer-7-reasons-why/
With rising concerns regarding climate change and the increased demand for electricity on power grids around the United States, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in the energy sector has emerged to enhance energy efficiency, foster sustainability, and optimize operations. AI is the development of machine learning and intelligent machines that perform tasks previously designated for humans. AI technologies enable energy stakeholders to identify alternative solutions for grid efficiency by compiling and reporting historical energy usage data, projecting future trends in energy consumption, and respond to changing infrastructure conditions and advances. AI promotes sustainable energy practices related to energy production and distribution, smart grids, predictive maintenance, optimized energy consumption, energy demand forecasting, and efficiency of renewable energy systems, creating a more resilient energy ecosystem for customers.
Some AI technologies are equipped with creating advanced algorithms that empower energy stakeholders to analyze data from a variety of sources such as user consumption habits, infrastructure performance and energy patterns, optimizing daily operations, detecting anomalies, and making data driven decisions to drive efficiency and sustainability in the industry.
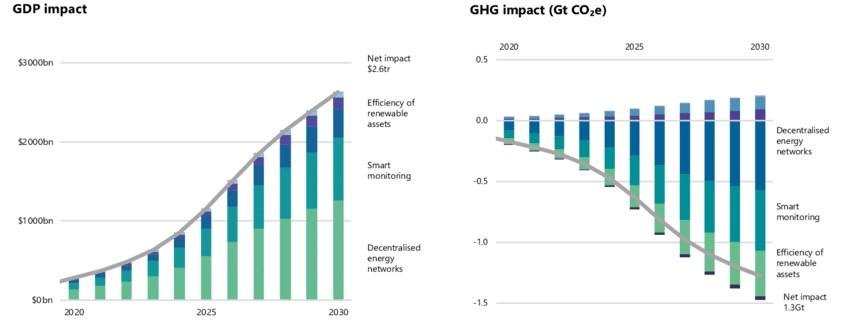
Data Dynamics, a data management and software company specializing in data analytics, has stated the importance of investments into AI technologies in the energy market for strategies around efficiency of renewable assets, smart monitoring, and decentralized energy markets. They project the change in the energy market is expected to grow steeply from 2020 to 2030, seen in the visual below. At the same time, greenhouse gas emissions are expected to fall by 0.1-0.3 percentage points year-over year as a result of increasing efficiencies from AI.
As with all new technologies, problems can arise from the use of AI. Integration of AI technologies into existing energy infrastructures, given the aging technology or operating systems, could lead to large investments to upgrade the infrastructure hardware and software necessary to minimize disruptions of integrating AI. Security and privacy of the sensitive data collected could be at greater risk of cyber threats and security breaches if measures to safeguard industry data are not thought through. Due to software coding in AI, it can raise ethical implications in terms of biases and fairness to customers for advanced systems, because biases are unknown until AI has been deployed for industry use. While there are still many challenges to be thought through for emerging AI in energy, this new technology presents an opportunity to address energy challenges and reduce environmental impacts.